How to Estimate Torque Without a Torque Wrench: Tips and Techniques

Do you need to tighten a bolt or loosen a nut but don’t have a torque wrench at hand? Don’t worry! You can still estimate the required torque with a few simple steps. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional mechanic, there are times when you may not have access to a torque wrench. However, it’s important to ensure that the nuts and bolts are tightened to the correct level to prevent damage or accidents.
So, how can you estimate the torque without a torque wrench? We’ve got you covered. In this blog, we’ll explore some simple yet effective ways of estimating torque that anyone can try.
Understanding Torque
If you’re unsure about how to estimate torque without a torque wrench, there are a few simple methods you can try. One way is to use a standard socket wrench and leverage your own strength to tighten the bolt. The amount of force you apply will depend on the size of the bolt, but you can estimate by considering the length of the wrench handle and the force you’re able to exert.
Another way to estimate torque is by using a bolt torque chart. This chart will provide you with the recommended torque for your specific bolt and size, based on industry standards. However, keep in mind that sometimes a different torque may be required based on the specific application or materials being used.
It’s important to always use caution and follow safety guidelines when working with torque, as over-tightening can lead to damage and potential injury.
Defining Torque
Torque is a measure of a force’s twisting ability around an axis. It is commonly used in engineering, physics, and mechanics to describe rotational motion. To better understand torque, consider the example of a door knob.
When turning the knob, you apply a force, or effort, to it. The door knob then applies a torque, or rotational force, to the door. This torque is what enables the door to open or close.
Torque is measured in units of Newton-meters (N-m) or foot-pounds (ft-lb), and it is important to consider both the magnitude of the force applied and the distance from the axis of rotation when calculating torque. In practical terms, torque is used in a variety of applications, from car engines to wind turbines to everyday tools like wrenches and screwdrivers. Understanding torque can help engineers and mechanics design and troubleshoot these systems more effectively.

Why Torque Matters in Fastening
When it comes to fastening materials together, understanding torque is crucial. Torque is a term used to describe the rotating force that is applied to a fastener when tightened. Simply put, it measures how tightly a bolt or screw is turned.
Having the correct torque is essential for ensuring that the fastener stays securely in place and that the material being fastened is held together with the appropriate amount of force. Torque can also affect the lifespan of a fastener as over-tightening can cause it to break or strip the threads, while under-tightening will not provide the necessary strength. To put it into perspective, think of twisting a jar lid on too tight or too loose – it’s all about finding that sweet spot where it is turned with just the right amount of force.
So, the next time you’re tightening a bolt or screw, remember that torque matters!
Factors Affecting Torque
Estimating torque without a torque wrench might seem like a daunting task, but it can be done if you have a basic understanding of the factors that affect torque. The primary factors that affect torque are the size of the fastener, the type of material it is made of, and the lubrication used. A larger fastener will generally require more torque than a smaller one.
Similarly, different materials require different amounts of torque to achieve the same level of fastening, with softer materials requiring less torque than harder ones. The lubrication used can also affect the level of torque needed, with less torque required when the threads are properly lubricated. By considering these factors, you can estimate the level of torque needed by taking into account the specific characteristics of the fastener, material, and lubrication being used.
With practice, you can develop a feel for the appropriate level of torque required, allowing you to tighten fasteners with confidence, even when a torque wrench is not readily available.
Thread Pitch
Thread pitch is an important factor in determining the torque requirements for a given application. Thread pitch is the distance between adjacent threads on a screw or bolt and can have a significant impact on the amount of torque necessary to achieve a desired level of clamping force. A finer pitch requires more torque than a coarser pitch to achieve the same level of clamping force.
This is because the finer pitch has a greater surface area in contact with the mating thread, resulting in increased friction. Other factors that can affect torque requirements include thread material, lubrication, and thread engagement length. When selecting fasteners for a particular application, it is important to consider all of these factors to ensure that the appropriate torque is applied and the fasteners are able to perform as intended.
Friction
Friction is an essential factor affecting torque, which is the force that causes rotational motion. Friction is the resistance to motion that occurs when two surfaces rub against each other. In terms of torque, it is the force needed to overcome the friction between two surfaces to produce rotational motion.
The coefficient of friction between two surfaces determines the frictional force acting on them. If the coefficient of friction is high, more torque is required to overcome the friction and produce rotational motion. Additionally, the surface area in contact, as well as the type of lubrication used on the surfaces, can also affect the friction and, therefore, the torque required for rotation.
It is essential to reduce friction to increase the efficiency of machines and reduce energy consumption. Proper lubrication and the use of smooth surfaces with lower coefficients of friction can significantly reduce torque requirements and increase machine efficiency.
Bolt Type and Size
When it comes to bolt torque, there are various factors that need to be taken into account. One of the most critical factors is the type and size of the bolts used. The size determines the thickness of the bolt, while the type influences its shape and features.
For instance, hex bolts are popular for their hexagonal shape that allows secure tightening. Meanwhile, carriage bolts have a square head that can prevent rotation during installation. Additionally, the grade or strength of the bolt affects the torque needed for fastening.
Higher-strength bolts require greater torque to achieve the desired clamping force and avoid loosening under operational stresses. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure you use the appropriate bolt type and size to achieve optimal torque and prevent potential failures or accidents.
Methods of Estimating Torque
If you don’t have a torque wrench, estimating the torque required can be difficult but not impossible. One method is to use a mathematical formula that involves the bolt’s size and the material’s friction. This formula estimates the torque required to achieve a given preload in the bolt.
However, it should be noted that this method is merely an approximation and may not provide the most accurate results. Another way to estimate torque is to use a torque-angle method. This involves tightening the bolt to a predetermined angle, which produces a specific amount of torque.
This method is more accurate but requires a bit of experience and some trial and error. In summary, while estimating torque without a torque wrench is possible, it is not an exact science, and the results may not be as accurate as those obtained using a torque wrench. However, with some trial and error using the methods mentioned above, you can get pretty close.
Using a Torque Calculator
A torque calculator is an essential tool for any mechanical engineering project or repair. There are several methods of estimating torque, all of which are critical for ensuring the safety and efficiency of any machinery. The most common way to estimate torque is to use a formula that takes into account the length of the lever arm, the force being applied, and the angle of rotation.
However, this method can be time-consuming and may not be accurate for more complex systems. Another popular method is to use a torque wrench, which measures the actual torque being applied to a bolt or nut. By using a calibrated wrench, engineers can ensure that they are applying the correct amount of torque to each fastener.
Ultimately, the most efficient way to estimate torque is by using a torque calculator. This tool takes all of the necessary inputs into account and provides a precise calculation of the required torque, saving time and ensuring accuracy. By using a torque calculator, engineers can complete their projects on time and with confidence in the safety and reliability of their work.
Using a Bolt Tightening Sequence
When it comes to tightening bolts, it’s important to use a methodical approach to ensure they’re tightened evenly and securely. One such approach is using a bolt tightening sequence, which involves tightening the bolts gradually and systematically in a specific order. This helps distribute the torque evenly and prevents uneven loading or stress on the bolts.
Estimating the correct torque for each bolt is also an important aspect of this process, as over-tightening can lead to damage and under-tightening can result in looseness and potential failure. There are various methods of estimating torque, including using torque wrenches, torque tables, and even angle tightening methods. Conducting regular maintenance and inspections to ensure bolts are properly tightened and torqued can help prevent accidents and breakdowns.
So next time you’re working with bolts, remember the importance of a good bolt tightening sequence and accurate torque estimation to keep things running smoothly.
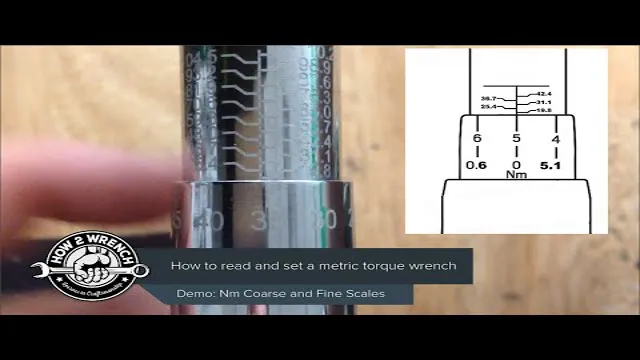
Using a Torque Chart
Estimating Torque When it comes to estimating torque, there are a few different methods to consider. One of the most common ways to estimate torque is by using a torque chart. This chart takes into account the material being used, the size of the fastener, and the thread pitch, providing a range of torque values to choose from.
Another method is to use a torque wrench, which applies a set amount of force to the fastener, allowing for precise torque to be applied. However, it is important to note that both of these methods rely heavily on accurate measurements and require a certain level of expertise to ensure proper torque is being applied. It is always best to consult the manufacturer’s specifications or consult with a professional to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Conclusion
So there you have it – a guide to estimating torque without a torque wrench. You may not be able to measure it to the exact decimal point, but with a little bit of practice, you can get pretty darn close! Remember, it’s all about applying the right amount of force and using your intuition. And who needs a pricey torque wrench anyway? Sometimes the best tools are those we carry with us all along – our brains and our hands.
Happy torque-ing!”
FAQs
What is torque and why is it important in mechanical systems?
Torque is a measure of rotational force and is important in determining the ability of a system to perform tasks such as rotating objects or tightening bolts.
Can torque be estimated without a torque wrench?
Yes, torque can be estimated by using a formula that takes into account the force being applied and the length of the lever arm.
How accurate are torque estimates without a wrench?
Torque estimates without a wrench can be accurate if the formula is used correctly and the force being applied is consistent.
What is the formula for estimating torque without a wrench?
The formula is torque = force x distance, where force is the amount of force being applied and distance is the length of the lever arm.
What are some common tools that can be used to estimate torque without a wrench?
Common tools include a torque app on a smartphone, a beam-style torque wrench, or a torque stick.
Can torque estimates be affected by the type of fastener being used?
Yes, torque estimates can be affected by the type of fastener being used, as different materials and sizes will require different torque specifications.
What are some tips for estimating torque without a wrench?
Tips include ensuring that the force being applied is consistent, using the correct formula for the task, and double-checking the torque specification for the particular fastener being used.