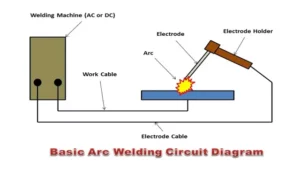
Welding is an essential process in many industries, and understanding the electrical currents involved is crucial for safe and effective welding. Electrical currents play a significant role in welding machines, determining their output and overall performance. As such, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of these currents to ensure that your welding operations go smoothly.
This blog post will delve into the basics of welding machines and electrical currents to help you grasp this essential welding concept and improve your welding skills. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s delve into the world of welding currents!
Overview
If you’re new to welding, you might be wondering whether the ground on a welding machine is positive or negative. The answer is that it depends on the type of welding machine you’re using. Most MIG and TIG welding machines have a negative ground, while stick welding machines have a positive ground.
The ground clamp is an essential part of the welding process since it connects the workpiece to the welding machine’s power supply. In essence, the ground clamp gives the electricity a pathway to flow through the workpiece and back to the welding machine. If you’re not sure which type of welding machine you have or how to set it up correctly, it’s always a good idea to read the manual or talk to an experienced welder.
Remember, proper setup and safety measures are crucial when welding, so don’t cut corners or take unnecessary risks.
Explanation of Welding Machine Electrical Currents
Welding machines use electrical currents to heat metals and join them together. These currents typically range from 50 to 500 amperes and can be either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). AC currents change direction periodically, while DC currents flow in one direction continuously.
AC currents are commonly used for welding aluminum, magnesium, and titanium due to their ability to prevent oxidation during the process. DC currents, on the other hand, are used for welding steel, copper, and other metals. In addition, welding machines may have variable voltage settings to adjust for different thicknesses of metal and gauge sizes.
By understanding the different types of electrical currents used in welding machines, welders can select the appropriate settings for their specific welding project and achieve high-quality, strong welds.
Importance of Grounding
Grounding is an essential aspect of life that is often overlooked. It refers to the connection between your body and the Earth. You may have experienced its benefits while walking barefoot on grass or feeling refreshed after swimming in the ocean.
The importance of grounding lies in its ability to balance the electromagnetic fields in your body and reduce the impact of harmful toxins and stressors. By grounding yourself, you are allowing the Earth’s energy to flow into your body, which can promote better sleep, reduce inflammation, and improve your overall well-being. Neglecting to ground yourself can result in feeling anxious, restless, and disconnected.
Incorporating more grounding practices into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature, can provide significant health benefits and improve your quality of life. Make sure to prioritize grounding to maintain a healthier and happier life.
Grounding in Welding Machines
When it comes to welding machines, the ground is extremely important for safety reasons. So, is the ground on a welding machine positive or negative? The answer is that it is neither. The ground on a welding machine serves to complete an electrical circuit and protect the welder from electric shocks.
It is not the same as the positive or negative charge on a battery or other electrical device. Without a proper ground, the electrical current could flow through the welder’s body, causing serious injury or even death. That is why it is essential to make sure your welding machine’s ground connection is secure and functioning correctly before you begin any welding operation.
Additionally, it is important to only use welding machines that are properly grounded and to follow all safety precautions to prevent accidents and injuries while welding.
Definition of Grounding
Grounding in welding machines is a fundamental safety precaution that must never be overlooked. In welding, grounding refers to the act of establishing an electrical pathway between the welding machine and the workpiece. This is important because welding generates high levels of electricity and heat, and if not handled carefully, can pose a significant hazard to the welder and anyone in the vicinity.
Without proper grounding, the welding machine may become energized, posing a risk of electric shock to the operator. Additionally, it may cause damage to the equipment, and lead to poor welding performance. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the welding machine is properly grounded for safe and effective welding operations.
Grounding in welding machines can be established using different methods, such as using a grounding cable, ground clamp, or a grounding rod. Regardless of the method chosen, the key is to ensure that the electrical circuit is complete and that there is a safe pathway for electricity to travel through. By doing so, the risk of electrical shock and hazards is significantly minimized, making the welding process safer for everyone involved.
Role of Grounding in Welding Machines
When it comes to welding machines, grounding plays a crucial role in their overall performance and safety. Grounding helps to establish a safe and secure electrical connection between the welding machine and the workpiece, which prevents electric shocks and damages from happening. Without proper grounding, the welding machine can become unstable and produce inconsistent results.
Additionally, it can pose a significant risk to the welder who is using the machine, as any electrical faults can result in shocks and injuries. When you ground a welding machine, you essentially provide a safe pathway for any stray electrical current to flow, rather than letting it build up in the welding machine or on the workpiece. This not only helps to prevent accidents but also ensures that the welding process is more efficient and effective.
In summary, grounding is an essential aspect of welding machines that should never be overlooked. It offers numerous benefits, including protection against electrical shocks and improved overall performance. By grounding your welding machine, you can ensure that your welding projects are done correctly and safely each time.
Types of Ground Connections
When it comes to welding machines, the ground connection is an essential component for the weld to be successful. However, the type of ground connection may vary depending on the specific welding machine being used. Generally speaking, the ground on a welding machine is negative, meaning that it operates as a cathode and attracts positively charged ions.
This negative charge helps to stabilize the heat and create a smooth weld. However, there are some welding machines that use a positive ground, such as some TIG welders. In these machines, the positive ground is used to create a stronger arc and to avoid the potential for electrical interference.
Regardless of the type of ground used, it is important to ensure that the ground connection is clean and secure to prevent any disruptions in the welding process.
Introduction to Types of Ground Connections
Ground connections are essential for many electrical systems, as they help protect against electrical shock and prevent damage to equipment. There are several types of grounding connections that can be used, including earth grounding, equipment grounding, and system grounding. Earth grounding involves connecting an electrical system to the earth through a ground rod or other metal conductor, which helps discharge any excess current.
Equipment grounding refers to connecting all metal components of an electrical system to a common ground, which helps protect against electrical shock. System grounding involves connecting one or more conductors from an electrical system to the earth, which helps stabilize the system’s voltage and provides a path for dissipation of currents. By understanding the different types of ground connections and their respective functions, electricians and other professionals can ensure the safety and proper functioning of electrical systems.
Grounding in Welding Machine- Types of Ground Connections
Grounding in welding machines is essential to ensure safety and optimal performance. In order to ground a welding machine, different types of ground connections can be used. The most common type of ground connection is the direct connection, where a copper cable is connected directly to a metal part on the welding machine and then to a grounding rod.
Another type of ground connection is the system ground, where the welding machine is connected to a neutral conductor in the electrical power supply system. This type of ground connection is often used in industrial settings where multiple machines are connected to the same electrical system. Finally, a third type of ground connection is the transformer ground, where the transformer is grounded separately from the welding machine.
This type of ground connection is often used in situations where the welding machine is located far from the power source. Choosing the right type of ground connection depends on the specific needs of the welding project and should be done by a trained professional. Overall, proper grounding in welding machines is crucial for safety and effective welding performance.
Identifying Polarity in Welding Machines
When it comes to welding machines, one common question that arises is whether the ground on the machine is positive or negative. The answer is that the ground on a welding machine is typically negative. However, it is important to note that some machines may have a positive ground, so it’s important to consult the owner’s manual or speak with a professional to determine the polarity of your specific machine.
The polarity of a welding machine is important because it determines the direction of the electrical current flow during the welding process. For example, with a negative connection, the electrode will become the cathode, producing a more stable and smoother arc. On the other hand, with a positive connection, the electrode will become the anode, resulting in a deeper and more penetrating arc.
Understanding the polarity of your welding machine is essential to achieving the desired results and producing quality welds.
Explanation of Welding Machine Polarity
Welding machine polarity can be confusing, especially for beginners. Essentially, polarity determines the flow of electricity from the welding machine to the welding wire or electrode. There are two types of polarity: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
DC polarity can be either straight or reverse, while AC polarity constantly changes. To identify polarity, look for the plus (+) and minus (-) signs on your welding machine. In general, DC reverse polarity is best for welding thick materials, while DC straight polarity is better suited for thinner materials.
AC polarity is typically used for welding aluminum or magnesium. It’s important to use the correct polarity when welding, as it can affect the quality of your welds and the overall efficiency of your welding process. By understanding and identifying the appropriate polarity for your welding needs, you can ensure successful and high-quality welds every time.
Testing Welding Machine Polarity
Welding machines are vital equipment in any welding work or metal fabrication. However, it is crucial to identify the polarity of the welding machine to establish which electrode connects to the positive and which hooks up to the negative. The polarity of the welding machine directly affects the welding process’s quality, particularly in terms of the weld’s penetration, cleaning, and deposition rate.
To identify the polarity of a welding machine or welding generator, you need a welding machine tester. This device connects to the welding machine’s positive and negative terminals to determine its polarity quickly. Furthermore, it is critical to check the electrode’s packaging or manufacturers’ labels to know the appropriate polarity for the welding electrode or filler metal type.
Establishing and testing the correct polarity of the welding machine can save you time and reduce the risk of defective welds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ground on a welding machine can be either positive or negative depending on the type of welding process being used. It’s like asking whether chocolate or vanilla is better – it all depends on personal preference and the desired outcome. So, whether you’re a positive or negative person, just make sure to always ground your welding machine properly for a safe and effective welding experience.
Keep on being electrically awesome, folks!”
Grounding and Polarity- Key Considerations
When it comes to welding machines, identifying polarity is an important consideration for ensuring successful and safe welds. Polarity refers to the direction in which electrons flow through the welding circuit, and can be either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). DC welding machines are typically either electrode positive (EP) or electrode negative (EN), with EP providing more heat at the electrode and EN providing more heat at the workpiece.
AC welding machines can also be used for certain types of welding, but require different techniques and equipment. In addition to polarity, proper grounding is also important for safety and effective welding. Ensuring that the welding machine is connected to a sturdy, well-grounded surface can help prevent electrical shocks and fires.
Overall, carefully considering polarity and grounding is crucial for achieving high-quality welds and maintaining a safe workplace.
Summary of Key Points
Identifying Polarity in Welding Machines When it comes to welding machines, it is crucial to understand the polarity of the current being used. The two types of polarity are DC and AC. DC polarity can be either straight or reverse, while AC polarity constantly alternates between positive and negative.
The polarity selection is important because it determines the welding machines’ electrode’s behavior when used to weld different materials. Some materials such as stainless steel and aluminum require reverse polarity, while others such as mild steel require straight polarity. Knowing how to identify the polarity of your welding machine and selecting the appropriate polarity for each project is essential for producing high-quality and long-lasting welds.
So, take the time to learn about polarity and its importance in welding machines, and you will improve the welding process.
FAQs
What is the purpose of polarity in welding?
Polarity refers to the direction of the electrical current flow in a welding machine. In welding, the polarity can be either positive or negative, and it affects the penetration, deposition rate, and overall quality of the weld.
Which is the most commonly used polarity for welding?
The most commonly used polarity in welding is DCEN, or Direct Current Electrode Negative. This means that the workpiece is connected to the positive terminal of the machine, and the electrode is connected to the negative terminal.
What is the difference between DCEN and DCEP in welding?
DCEN stands for Direct Current Electrode Negative, where the electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the machine. In contrast, DCEP stands for Direct Current Electrode Positive, where the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the machine. The main difference is in the welding characteristics, where DCEN produces deeper penetration, while DCEP provides better deposition rate and cleaning action.
Can AC be used for welding, and what is its polarity?
Yes, AC (Alternating Current) can be used for welding, but it does not have polarity in the same way that DC does. AC alternates between positive and negative electrodes rapidly, which can lead to a broader bead profile and increased spatter.
How do you determine the correct polarity for a welding application?
The correct polarity for a welding application depends on the type of welding, the material being welded, and the electrode used. It is important to consult the welding machine manual or an experienced welder to determine the best polarity for the job.
What is the effect of switching polarity during welding?
Switching polarity during welding can lead to changes in the penetration, deposition rate, and overall quality of the weld. It is generally advisable to stick to one polarity throughout the welding process, instead of switching back and forth.
Can the polarity of a welding machine be reversed, and how is it done?
Yes, the polarity of a welding machine can be reversed by switching the leads that connect the electrode holder and workpiece clamps to the machine. This process varies depending on the type of welding machine, so it is important to consult the manual or seek professional guidance.