Have you ever wondered how welding machines work? It’s an intriguing question that leaves many of us scratching our heads. Well, fear not because we’re here to demystify this process for you. Welding machines are fascinating tools that have revolutionized the world of metal fabrication.
They work by using electricity to create a high heat source that melts metal and fuses it together. It’s like magic in action! Think of welding machines as a cross between a chef’s torch and a glue gun. The electricity generates heat, like the flame from a torch, while the welding rod acts as a glue stick, binding the metal together as it cools.
This heated metal fuses with the weld rod, creating a bond that is often stronger than the original material. And the best part? You can weld virtually any kind of metal, from steel to aluminum, and even copper and brass. But how do welding machines create this heat source? That’s where the science comes in.
Welding machines use an electrical circuit to generate a powerful electric current that flows through the welding rod. This high amperage generates heat at the point of contact, which in turn melts the metal. Welders can control the heat output by adjusting the machine’s settings, ensuring they get the perfect temperature for the job at hand.
So there you have it, a brief overview of how welding machines work. From construction workers to artists, these machines have become staples in the metalworking industry. The welding process is a true feat of engineering and craftsmanship, creating strong bonds that can last a lifetime.
Now you know the science behind the sparks and flames, and you can appreciate just how amazing these machines really are.
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how welding machines work? Well, it all comes down to electricity and heat. Welding machines use electricity to generate heat that melts and binds metals together. The welding process happens in four steps: power supply, electrode, arc, and weld pool.
The power supply creates an electric current that flows through the electrode, creating an arc. This arc acts as a heat source, melting the metal pieces that are being welded. As the metal pieces melt, they combine to form the weld pool.
The weld pool is left to cool and harden, creating a strong bond between the two pieces of metal. There are different types of welding machines, including TIG, MIG, and Stick welding machines, which vary in their power source, electrode, and arc. By mastering the welding process, skilled welders can create a wide range of objects, from skyscrapers to sculptures.
With the right tools and techniques, welding can be a fascinating and satisfying craft. So, the next time you see a welded object, take a moment to appreciate the skill and knowledge that went into its creation. And if you’re interested in learning more, check out how welding machine works animation to see the welding process in action.
Explaining welding machines
Welding machines are an essential tool used to join or fuse two materials together, typically metals. These machines produce an intense heat source that melts and fuses the materials together, forming a strong bond. Welding machines come in various forms, from manual to automated, and use different welding methods such as MIG, TIG, or stick welding.
They are commonly used in various industries, including construction, automobiles, and shipbuilding. Each welding machine has its own unique features and capabilities, making it important to choose the right one for the desired application. Selecting the right type of welding machine can make all the difference in delivering high-quality welds that meet industry standards and increase productivity while minimizing errors and material waste.

Importance of knowing how it works
Knowing how something works is crucial in every aspect of life, and technology is no exception. The importance of understanding the intricacies of technological systems cannot be overstated as it helps to solve problems, improve efficiency, and avoid potential issues. By having a deeper understanding of how technology works, users can better navigate its features, troubleshoot problems, and make informed decisions regarding upgrades or purchases.
For example, if you understand how your smartphone functions, you can easily identify why it’s running slowly and implement solutions to fix the issue. The same applies to other technological devices and systems. In essence, knowing how technology works empowers users to use it effectively and proactively.
The Basics of Welding Machines
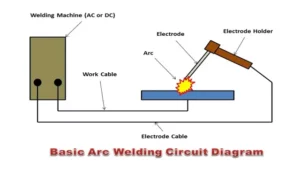
When it comes to welding machines, understanding how they work can seem complex at first. However, with the help of an animation, the basics become much easier to grasp. Welding machines work by using an electric current to create a welding arc between the metal being welded and the electrode.
This arc heats and melts the metal surfaces, which then cool and fuse together to create a strong bond. The welding machine has multiple components, including a power source, electrodes, cables, and a welding torch. When powered on, the machine generates an electric current, which flows from the power source through the cables and into the welding torch.
The electrode, which is positioned in the torch, carries the current and creates the arc when it comes into contact with the metal. Depending on the type of welding machine, there are various settings and adjustments that can be made to control the current and temperature, ensuring a precise and efficient weld. With practice and experience, welding with a machine becomes more intuitive, and you can create wonderful, intricate welds with ease.
Types of welding machines
When it comes to welding machines, there are several types to choose from depending on the specific welding task at hand. One of the most commonly used welding machines is the stick welding machine. This type of machine uses a consumable electrode that melts and fuses with the base metal to create a strong bond.
Another popular machine is the MIG welding machine, which uses a wire electrode and a shielding gas to create a clean and precise weld. TIG welding machines, on the other hand, use a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a separate filler material to create an extremely precise weld. And finally, there are plasma cutting machines, which use a plasma torch to cut through metal materials with a high level of accuracy.
Each of these machines has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one for your welding needs can make all the difference in achieving a high-quality weld.
Description of parts and components
When it comes to welding, welding machines are an integral part of the process. A welding machine is responsible for generating an electric arc that melts the metal to create a bond between them. The machine consists of various parts and components that work together to create a stable and efficient welding process.
The most crucial part of a welding machine is the power source, which provides the necessary voltage and current to create the electric arc. Other critical components include the electrode holder, which holds the welding rod in place, and the grounding clamp, which ensures a proper electrical connection to the metal being welded. The welding machine also has a cooling system to prevent overheating and extend its lifespan.
Moreover, a control panel with knobs and dials allows the operator to adjust the voltage, amperage, and heat level to ensure optimal performance. Overall, understanding the basics of a welding machine is crucial for any welder, as it enables them to make informed decisions and troubleshoot problems more effectively.
How they are powered
Welding machines are powered in different ways, depending on the specific type of machine. Some welding machines use AC (alternating current) power, while others use DC (direct current) power. The power source can also vary, with some machines being powered by electricity from an outlet, while others are powered by batteries or generators.
There are also machines that use gas, such as argon, to power the welding process. The type of power and power source used will depend on factors such as the type of welding being done, the materials being welded, and the location where the welding is taking place. It’s important to choose the right welding machine for your needs to ensure a successful welding process, whether it’s for personal or professional use.
The Welding Process
If you’ve ever wondered how welding machines work, the answer lies in a simple yet complex process. In essence, a welding machine generates an electrical current which is then used to heat metals until they melt and fuse together. This is accomplished by running an electric current through the metal, creating a circuit that generates heat and molten metal at the point of contact.
The welding machine produces the electrical current necessary for this to occur, either by using a transformer or an inverter to create an arc, which then melts the metal. The process is highly technical and requires skill and knowledge to execute correctly. However, with the right training and experience, a skilled welder can create strong, permanent welds in a variety of materials.
So next time you see a welder at work, now you know a little more about the science behind the process!
Preparing the workpiece and electrodes
When it comes to the welding process, proper preparation of the workpiece and electrodes is essential. Before beginning any welding project, it’s important to clean the workpiece thoroughly to remove any dirt, rust, or other debris. This will ensure a strong bond between the two pieces being welded together.
Additionally, the electrodes must be properly prepared before use. This includes sharpening or cleaning any dull or dirty electrodes and ensuring they are the correct size for the project. A properly prepared electrode will help to create a consistent and clean weld, while a poorly prepared one can lead to weak or incomplete welds.
So, take the time to properly prepare both the workpiece and electrodes to ensure a successful welding project.
Starting the weld
Starting the weld is a crucial step in the welding process. Before beginning, it’s essential to ensure you have all the necessary equipment, including your welding machine, power source, and safety gear. Once you’re ready, the first step is to prepare the surface to be welded by cleaning it of any dirt, rust, or other contaminants.
This will ensure that the weld will be strong and of good quality. After cleaning, set up the welding machine and adjust the settings based on the metal being welded. Once you’ve done that, it’s time to start the weld.
Make sure that you have a stable position with proper balance and posture. Begin by striking an arc between the welding electrode and the metal, and then move it smoothly along the joint to create a consistent weld bead. Starting the weld correctly is essential to ensure a successful welding process, so take your time to get it right.
Remember, practice makes perfect!
Heat control and melting the material
When it comes to welding, the process involves melting and joining materials through heat control. The heat generated must be sufficient to cause the material to melt and fuse together. However, overheating can lead to deformities, weakening of the joint, or even complete failure.
The welding process typically uses an intense heat source, such as a plasma arc or a flame, to bring the materials to their melting point. Once melted, the materials are joined together, and the resulting joint solidifies again as the material cools. It’s essential to use the right techniques and equipment for a successful weld.
Welding is commonly used in manufacturing processes and in construction to join metal, plastic and composite parts. Proper heat control and melting technique is crucial to achieve strong, durable and long-lasting welds.
Finishing the weld and cooling down
After the welding process is complete, it’s crucial to finish the weld and cool it down properly. This involves the use of tools such as a wire brush or chipping hammer to clean the weld area and remove slag or spatter. Next, the weld should be inspected to ensure it meets industry standards and that there are no defects such as cracks or porosity.
Once the weld has been deemed satisfactory, the cooling process can begin. This can be done by allowing the weld to air-cool or utilizing water or oil quenching methods to speed up the process. It’s important to note that rapid cooling can cause the weld to become brittle and prone to cracking, so it’s essential to follow proper cooling protocols to avoid any potential issues.
By properly finishing and cooling down the weld, you can ensure that it is strong, durable, and long-lasting, making it safer and more reliable for its intended use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the welding machine is like a fiery dance between electricity and metal. Like a seasoned tango couple, they fuse together, creating a bond that stands the test of time. The welding machine ignites a spark of innovation and creativity, allowing us to build a world where everything is possible.
So let’s raise our welding helmets to this magnificent process and continue to spark our imagination with its mesmerizing moves.”
Summary and benefits of understanding how welding machines work
Understanding how welding machines work can provide numerous benefits, especially if you work in the welding industry. The welding process is a complex one, and knowing how welding machines operate can help you produce high-quality welds efficiently and safely. Welding machines generate an electrical current that passes through the metal, producing heat that melts the metal and fuses it together.
Many factors contribute to the efficiency of the welding process, such as the type of welding machine, the type of metal being welded, the settings of the welding machines, and the skill of the operator. Familiarizing yourself with these factors can help you produce welds with minimal waste and maximum precision. Furthermore, knowing how welding machines work can help you select the appropriate welding machine for the job, potentially saving you time and money.
Overall, learning about welding machines and the welding process can improve your productivity, accuracy, and safety, making your work more efficient and enjoyable.
FAQs
What is welding machine?
A welding machine is a device that is used to join or fuse two materials, typically metals, with heat and pressure.
How does a welding machine work?
A welding machine works by producing an electric arc between an electrode and the metal being welded. The heat generated by the arc melts the metal, creating a weld that fuses the two pieces of metal together.
What types of welding machines are there?
There are several types of welding machines, including stick welders, MIG welders, TIG welders, plasma cutters, and spot welders.
How does a stick welder work?
A stick welder uses an electrode that is coated in flux to create an arc between the electrode and the metal being welded. The heat from the arc melts the electrode, creating a weld that fuses the two pieces of metal together.
What is a MIG welder?
A MIG welder uses a spool of wire to create an arc between the wire and the metal being welded. The wire is fed through a gun, and the heat from the arc melts the wire and the metal, creating a weld that fuses the two pieces of metal together.
How does a TIG welder work?
A TIG welder uses a tungsten electrode to create an arc between the electrode and the metal being welded. The heat from the arc melts the metal, and a separate filler rod is added to create the weld.
What is plasma cutting?
Plasma cutting is a process that uses a plasma cutter to cut through metal. The plasma cutter creates an electric arc that ionizes gas and creates a plasma, which melts the metal and cuts through it.